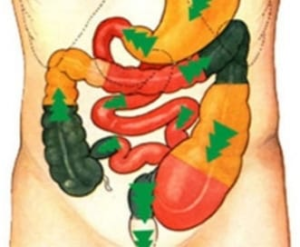
Panchakarma Procedure
Panchakarma is a traditional Ayurvedic method of detoxification and rejuvenation. It is a comprehensive therapeutic approach that aims to cleanse the body of toxins and restore balance among the bodily humors (doshas). Panchakarma treatments are tailored to individual needs and commonly include herbal therapies and specialized massages. The objective is to support both physical and mental well-being in accordance with Ayurvedic principles.
Concept in Ayurveda
According to Ayurveda, health is defined not merely as the absence of disease, but as a state where the doshas (Vata, Pitta, Kapha), dhatus (tissues), agni (digestive fire), and malas (waste products) function normally. Additionally, a healthy individual is described as one whose soul (atma), sense organs (indriya), and mind (manas) are in a state of harmony.
The Three Doshas
The Ayurvedic system categorizes bodily functions into three doshas which is impact human body:
-
Vata (movement)
-
Pitta (transformation)
-
Kapha (structure)
According to ayurved each dosha governs specific physiological and psychological functions. An imbalance in these doshas is believed to cause disease.
Vata Dosha
-
Dry (Ruksha)
-
Light (Laghu)
-
Cold (Shita)
-
Rough (Kathina)
-
Subtle (Sukshma)
-
Mobile (Chala)
Pitta Dosha
-
Hot (Ushna)
-
Sharp (Tikshna)
-
Light (Laghu)
-
Oily (Snigdha)
-
Liquid (Drava)
-
Spreading (Vishada)
Kapha Dosha
-
Heavy (Guru)
-
Cold (Shita)
-
Oily (Snigdha)
-
Slow (Manda)
-
Stable (Sthira)
-
Soft (Mrudu)
Panchakarma Overview
The term “Panchakarma” translates to “five actions” or “five procedures.” These therapeutic measures aim to remove toxins after the body has been prepared through oleation and fomentation. So panchakarma serves preventive, curative, and promotive roles in health care.
The Five Karmas
The five main procedures target different parts of the body:
1. Vamana Karma (Therapeutic Emesis)
A method to eliminate excess Kapha through controlled vomiting. It is often indicated for conditions like asthma, chronic colds, and sinus congestion.
2. Virechana Karma (Purgation Therapy)
This involves purgation to expel excess Pitta dosha, mainly targeting the small intestine and liver. It is used for conditions such as jaundice, skin disorders, and chronic digestive issues.
3. Basti Karma (Medicated Enema)
Basti involves the administration of medicated oils or herbal decoctions through the rectum. Practitioners primarily use it to treat Vata-related disorders such as arthritis, neurological conditions, and constipation.

4. Nasya Karma (Nasal Therapy)
This procedure administers medications via the nasal route to treat conditions affecting the head and neck, including hair loss, migraines, and sinus issues.

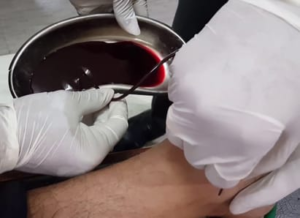
5. Raktamokshana (Bloodletting Therapy)
This process involves the removal of impure blood to treat disorders caused by blood impurities.

Panchakarma Stages
Practitioners conduct Panchakarma in three distinct stages:
A. Poorva Karma (Preparatory Phase)
Involves Snehan (oleation) and Swedan (fomentation) to loosen toxins and prepare the body.
B. Pradhan Karma (Main Treatment)
The doctor selects the primary detoxification procedure based on the location and nature of the dosha imbalance.
C. Paschat Karma (Post-Therapy)
This is a recovery phase focusing on diet and lifestyle to restore digestive and metabolic balance.
Reference: Basic Introduction about Panchkarma